Azure Quickstart Templates: A Great Resource for Learning ARM Templates
Azure Quickstart Templates are a great resource for learning ARM templates. They are provided by the Azure community and cover a wide range of scenarios.
What are Quickstart templates?
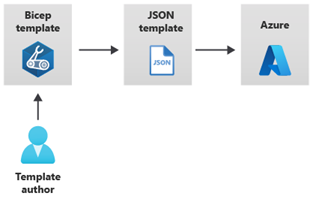
Quickstart templates are Azure Resource Manager templates that are provided by the Azure community. They are designed to help you get started with Azure quickly and easily.
What do Quickstart templates include?
Quickstart templates typically include the following files:
azuredeploy.json: This file defines the resources that will be deployed.
azuredeploy.parameters.json: This file provides the values the template needs.
How to use Quickstart templates
To use a Quickstart template, you can follow these steps:Download the template from the Azure Quickstart Templates repository.
Open the template in a text editor.
Review the README.md file to learn more about the template.
If necessary, modify the azuredeploy.parameters.json file to provide the values the template needs.
Deploy the template using the Azure CLI or PowerShell.
Where to find Quickstart templates
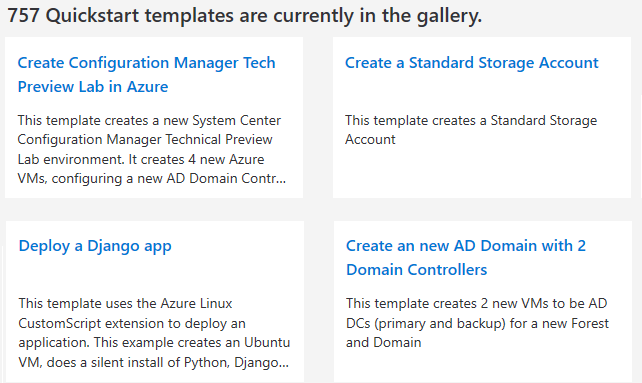
You can find Quickstart templates in the Azure Quickstart Templates repository. The repository is organized by language and technology.
Why use Quickstart templates?
There are several reasons why you might want to use Quickstart templates:They are a great way to learn ARM templates. The README.md files in Quickstart templates provide a good overview of how the templates work.
They can save you time. Quickstart templates can help you get started with Azure quickly and easily.
They are well-tested. Quickstart templates are tested by the Azure community before they are published.
If you are new to ARM templates, I encourage you to check out the Azure Quickstart Templates repository. There are a number of great templates that can help you get started with Azure quickly and easily.